Advantages of 3T over 1.5 Telsa MRI Scan
When comparing 3 Tesla (3T) MRI scanners to 1.5 Tesla (1.5T) systems, several advantages arise due to the higher magnetic field strength. Here are the key benefits of 3T MRI over 1.5T:
1. Higher Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
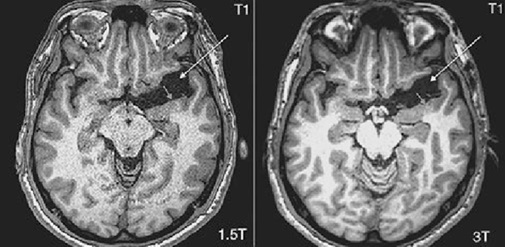
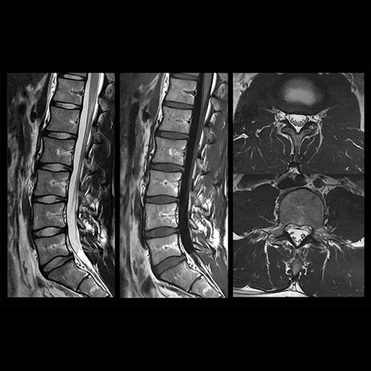
The stronger magnetic field of 3T produces a higher signal-to-noise ratio, leading to sharper and more detailed images.
This is particularly beneficial for imaging small structures (e.g., brain vasculature, musculoskeletal details, and small tumors).
2. Improved Spatial Resolution
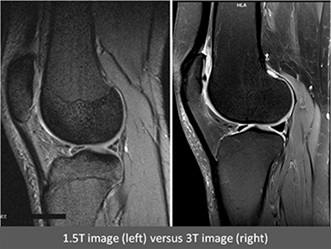
The increased SNR allows for finer spatial resolution, enabling better visualization of fine anatomical structures.
Useful in neurological imaging (e.g., multiple sclerosis plaques, hippocampal atrophy), musculoskeletal imaging (e.g., cartilage, tendons), and oncology (small lesions).
3. Faster Imaging (Reduced Scan Times)
Due to the stronger signal, 3T can acquire images faster than 1.5T while maintaining image quality.
Helpful for dynamic studies (e.g., fMRI, cardiac MRI, perfusion imaging) and reducing motion artifacts.
4. Better Functional and Metabolic Imaging
fMRI (functional MRI): 3T provides better BOLD (Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent) contrast, improving brain mapping for neurosurgical planning and research.
Spectroscopy (MRS): Higher field strength allows for better spectral resolution, aiding in metabolic profiling of tumors and neurological disorders.
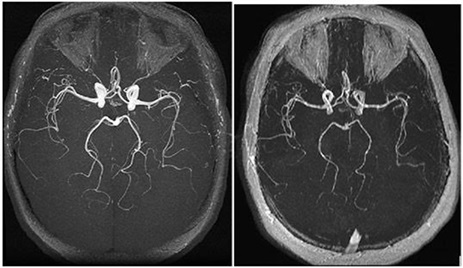
5. Enhanced Angiography (MRA & MRV)
3T MR angiography (MRA) offers superior vessel contrast and resolution, improving detection of small aneurysms, stenoses, and vascular malformations.
Time-of-flight (TOF) MRA benefits significantly from the higher field strength.
6. Improved Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI) & Tractography
Higher sensitivity in detecting acute ischemia (stroke imaging).
Better fiber tracking in DTI (Diffusion Tensor Imaging) for neurosurgical and neurological applications.
7. Better Contrast in Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging (SWI)
Enhanced detection of microbleeds, calcium, and iron deposits (important in traumatic brain injury, neurodegenerative diseases, and stroke).
Disadvantages & Considerations of 3T:
Higher cost (both acquisition and maintenance).
Increased susceptibility artifacts (e.g., near metal implants, air-tissue interfaces).
Higher specific absorption rate (SAR), leading to potential heating concerns (requires careful protocol optimization).
Not always necessary for routine imaging (1.5T may suffice for many clinical applications).
When is 3T Preferred Over 1.5T?
Neuroimaging (epilepsy, small tumors, multiple sclerosis, fMRI).
Musculoskeletal MRI (cartilage, ligaments, small joints).
Oncology (detecting small metastases, prostate MRI, breast MRI).
Research applications (high-resolution brain mapping, advanced spectroscopy).
Conclusion:
While 3T MRI offers superior image quality, resolution, and advanced imaging capabilities, 1.5T remains widely used for routine clinical scans due to its lower cost, fewer artifacts, and sufficient diagnostic quality for many conditions. The choice depends on the specific clinical or research need.