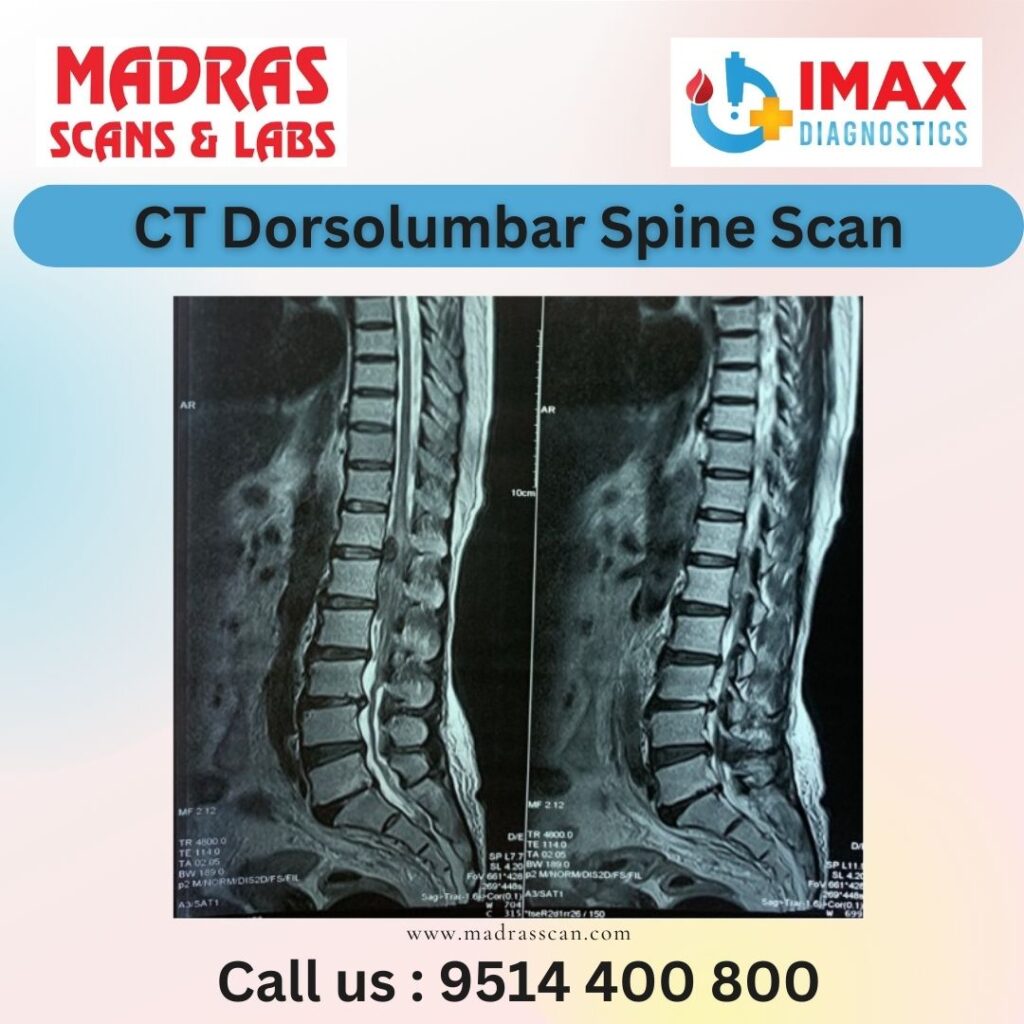
CT (computed tomography) scan of the dorso-lumbar spine is a diagnostic imaging procedure used to visualize the bones, discs, spinal cord, and surrounding tissues in the middle and lower back region. It can help diagnose various conditions such as fractures, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, tumors, infections, and other abnormalities affecting the spine.
During a CT scan of the dorso-lumbar spine, a series of X-ray images are taken from different angles around the body, and a computer processes these images to create cross-sectional slices or 3D images of the spine. This provides detailed information about the structure and condition of the spine, helping healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.

Some common uses of CT dorso-lumbar spine scans include:
Evaluation of back pain: CT scans can help identify the cause of back pain, such as fractures, herniated discs, or spinal abnormalities.
Assessment of trauma: CT scans are often used in emergency settings to evaluate traumatic injuries to the spine, such as fractures or dislocations.
Diagnosis of degenerative conditions: CT scans can detect degenerative changes in the spine, such as arthritis, spinal stenosis, or disc degeneration.
Pre-surgical planning: CT scans provide detailed anatomical information that can help surgeons plan spinal surgeries, such as spinal fusion or decompression procedures.
Monitoring treatment: CT scans may be used to monitor the progress of treatment for spinal conditions, such as assessing the healing of fractures or evaluating the effectiveness of chemotherapy or radiation therapy for spinal tumors.
Overall, CT dorso-lumbar spine scans are valuable tools for diagnosing and managing a wide range of spinal conditions, providing detailed images that help healthcare providers deliver optimal care to patients.
